Data Type In Java with example program
Unlike c++,Java is a strongly typed language. Data type is used to declare a variable.
Every variable should be declared before using that variable in the program.
A data type defines a set of values and the operation that can be performed on them.
There are two types of data types available in Java.
Primitive data type (also known as value type)
In primitive data type size is predefined and stored in stack memory
Non Primitive data type(also known as reference data type)
Reference data type stored in heap memory this type is not predefined
Primitive data type
Boolean —> Boolean data type consists of two values true/false,by default it is false
Size of Boolean variable is one bit
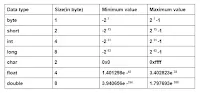
byte —> very small integer
short —> small integer
int —> integer number
long —> big integer number
char —> 0 to 9,a to z(uppercase and lowercase)special symbol
float —> floating number(single precision, means that 6 or 7 digit fractional part)
double —> big floating number(double precision, means that 14 or 15 digit fractional part)
Non primitive data type
String —> string is a group character
Array —> collection of elements of same data types
Class —> consists of variables and methodsData types in java example program
class DatatypeExample
{
public static void main(String a[])
{
byte b_value=126;
short s_value=32767;
int i_value=221133;
long l_value=55334422;
float f_value=3.14f;
double d_value=4.888;
char ch='a';
boolean bln=true; //true or false value only
System.out.println("java data type example program");
System.out.println(b_value);
System.out.println(s_value);
System.out.println(i_value);
System.out.println(f_value);
System.out.println(d_value);
System.out.println(b_value);
System.out.println(ch);
System.out.println(bln);
System.out.println("observe the output value carefully");
}
}
command line argument in java


Comments
Post a Comment